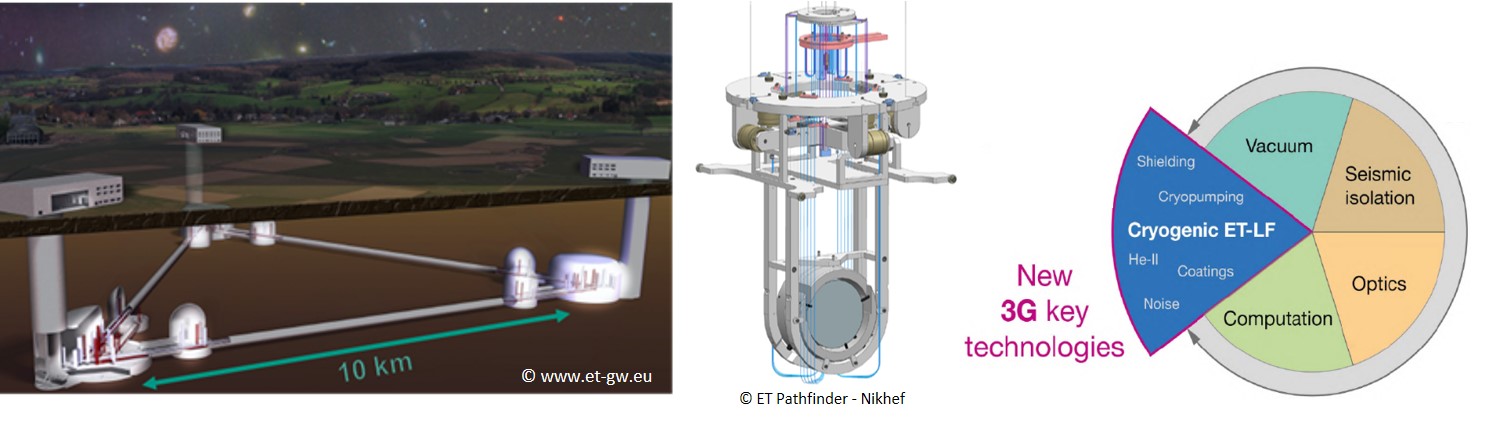
Conceptual design of a test facility for the cryogenic payload of the low-frequency interferometer in the Einstein Telescope
- Ansprechpartner:
- Starttermin:
März 2021
The Einstein Telescope (ET) is a third-generation gravitational wave detector (GWD), which is planned to be built in Europe as a large research infrastructure from 2025+. Compared to present second-generation GWD operated at room-temperature, the low-frequency (LF) interferometer in the Einstein Telescope will be operated at cryogenic temperatures around 10 - 20 K. Some of the particular challenges of this new technology include the provision of an ultra-low noise cooling system, the design of the heat path to extract the heat load during cool-down and in nominal operation in an ultra-high vacuum environment and the prevention or regeneration of particle adsorption on the cold mirror surface. Due to these challenges, the cryogenic payload of the ET-LF interferometer requires a complete re-design compared to the existing room-temperature design solutions. The definition of system specifications requires a strong interaction with the Optics Division, Suspension Division and the Vacuum & Cryogenics Division in ET in order to guarantee that all important aspects are considered and accessible for experimental investigation. (based on Einstein Telescope Design Report Update 2020)